what are the three phases of interphase Cell cycle interphase mitosis diagram stages biology cytokinesis figure anaphase metaphase phase g2 g1 division during cells stage dna mitotic
The process of cell division, specifically mitosis, is a fascinating and essential aspect of biology. In this post, we will delve into the intricacies of interphase and mitosis, exploring the different stages and their significance in the growth and development of living organisms.
Interphase: Preparing for Division
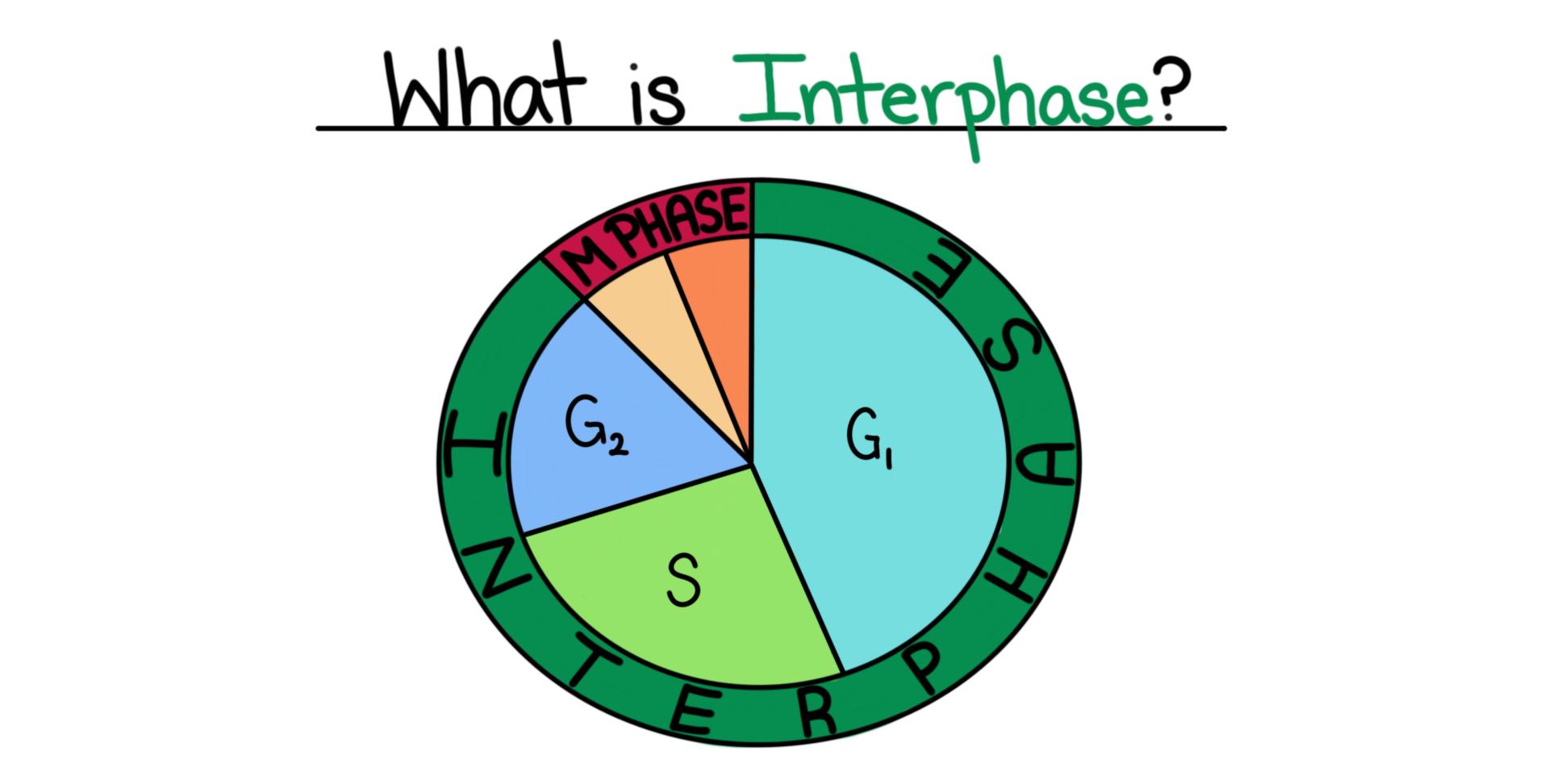
Before diving into mitosis, let’s first discuss interphase. Interphase is the longest phase of the cell cycle, accounting for approximately 90% of the total cycle duration. During this phase, the cell prepares itself for division by increasing its size, duplicating its DNA, and organelles.
Within interphase, distinct subphases can be identified. These include G1, S, and G2 phases. The G1 phase is characterized by cell growth and protein synthesis. The S phase follows, during which the DNA replicates, ensuring that each new cell will possess an identical copy of genetic information. Finally, the cell enters the G2 phase, where it continues to grow, prepares for division, and checks for any damaged DNA that may have occurred during replication.
Mitosis: Ensuring Accurate Cell Duplication
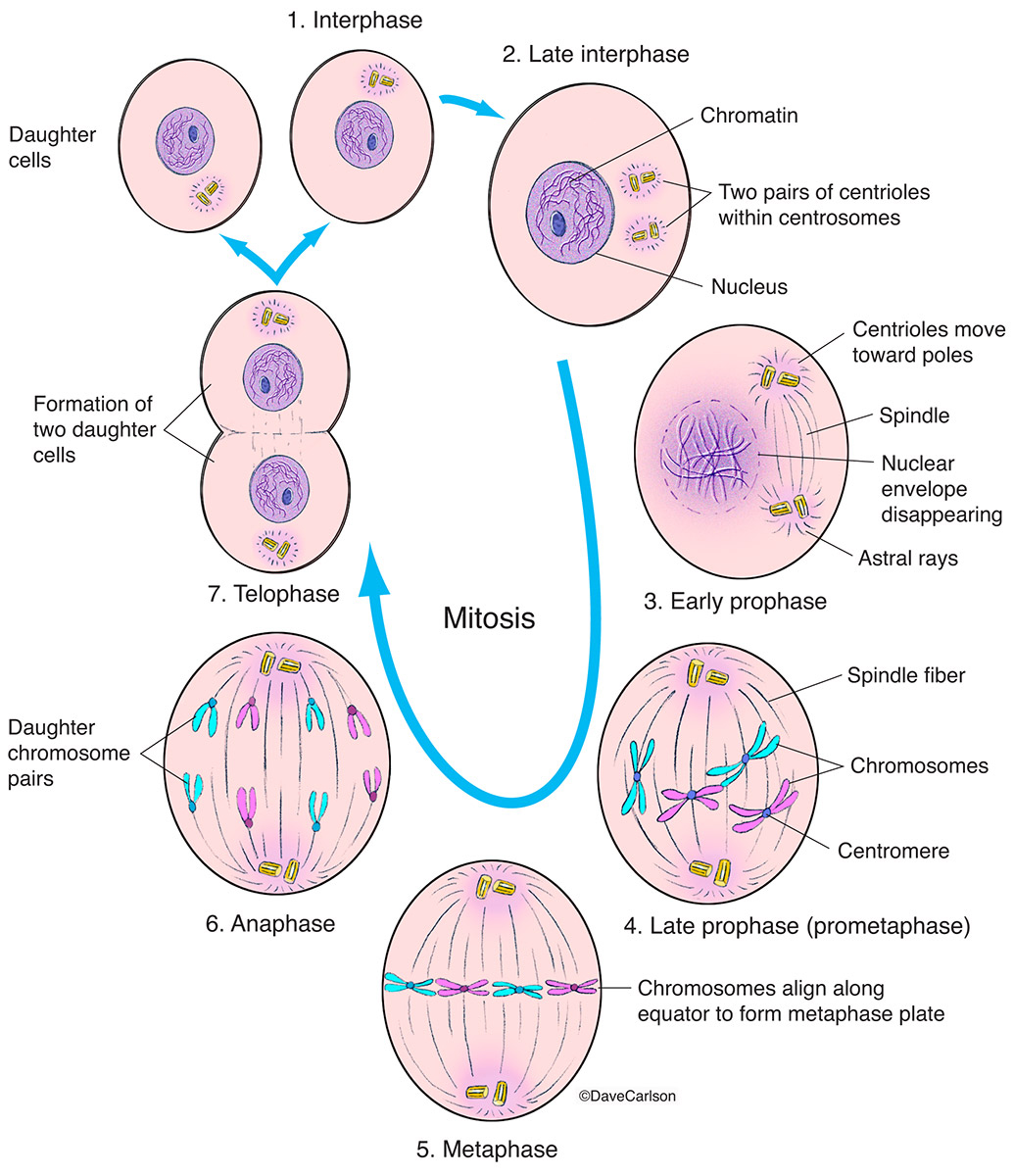
Once interphase is complete, the cell enters mitosis, a process that consists of several distinct stages. Mitosis plays a crucial role in cell duplication, allowing organisms to grow, repair damaged tissues, and replace aging cells.

The first phase of mitosis is prophase, during which the chromatin condenses into visible and distinct structures called chromosomes. The nuclear envelope dissolves, and spindle fibers begin to form, helping to organize the chromosomes. Next comes metaphase, where the chromosomes align at the center of the cell, forming the metaphase plate.
Anaphase follows, characterized by the separation of sister chromatids. The spindle fibers pull the chromatids apart and guide them towards the opposite ends of the dividing cell. The final stage of mitosis is telophase, during which new nuclear envelopes form around the separated chromosomes, forming two distinct nuclei.
Cytokinesis, the physical splitting of the cell, typically occurs at the end of mitosis. This process results in two genetically identical daughter cells, each with its own nucleus and complete set of chromosomes.
The Significance of Mitosis
Mitosis is vital for various biological processes. First and foremost, it contributes to the growth and development of living organisms. During embryonic development, mitosis facilitates the rapid cell division necessary for the formation of complex structures, tissues, and organs.
Mitosis also plays a crucial role in tissue repair and replenishment. For example, when you cut your skin, mitosis ensures that new cells are quickly produced, allowing the wound to heal. Without mitosis, our bodies would struggle to regenerate damaged or compromised tissues effectively.
Furthermore, mitosis ensures that each daughter cell receives an accurate and complete set of chromosomes. This process prevents the loss or gain of genetic material, which could potentially lead to harmful mutations or genetic disorders.
In conclusion, interphase and mitosis are fundamental processes in the cell cycle. Interphase prepares the cell for division, while mitosis ensures accurate cell duplication, facilitating growth, repair, and development. Understanding these processes allows us to appreciate the complexity and importance of cell division in maintaining the balance of life.
If you are searching about What Is Interphase? — Overview & Diagrams - Expii you’ve visit to the right web. We have 5 Pics about What Is Interphase? — Overview & Diagrams - Expii like What Happens During Interphase Of A Cell Cycle? | Science Trends, What Is Interphase? — Overview & Diagrams - Expii and also The Cell Cycle | Biology for Majors I. Here you go:
What Is Interphase? — Overview & Diagrams - Expii
 www.expii.cominterphase diagrams gabi
www.expii.cominterphase diagrams gabi
10.2A: Interphase - Biology LibreTexts
 bio.libretexts.orginterphase cell cycle biology phase stages 2a mitotic gap
bio.libretexts.orginterphase cell cycle biology phase stages 2a mitotic gap
The Cell Cycle | Biology For Majors I
 courses.lumenlearning.comcell cycle interphase mitosis diagram stages biology cytokinesis figure anaphase metaphase phase g2 g1 division during cells stage dna mitotic
courses.lumenlearning.comcell cycle interphase mitosis diagram stages biology cytokinesis figure anaphase metaphase phase g2 g1 division during cells stage dna mitotic
Interphase & Mitosis | Carlson Stock Art
 www.carlsonstockart.cominterphase mitosis cell meiosis stage dna reproduction asexual science life biology general
www.carlsonstockart.cominterphase mitosis cell meiosis stage dna reproduction asexual science life biology general
What Happens During Interphase Of A Cell Cycle? | Science Trends
 sciencetrends.comcycle cell interphase mitosis division cells eukaryotic events phases during biology happens prophase stages diagram kind meiosis pdf main figure
sciencetrends.comcycle cell interphase mitosis division cells eukaryotic events phases during biology happens prophase stages diagram kind meiosis pdf main figure
Cycle cell interphase mitosis division cells eukaryotic events phases during biology happens prophase stages diagram kind meiosis pdf main figure. Interphase diagrams gabi. Cell cycle interphase mitosis diagram stages biology cytokinesis figure anaphase metaphase phase g2 g1 division during cells stage dna mitotic